Iris Scan vs Retina Scan: What's the Difference and Which Is Better?
Iris scans capture the colored part of the eye using infrared light, while retina scans map blood vessel patterns at the back of the eye. Both are highly accurate biometric methods, but iris scanning is faster, more user-friendly, and widely adopted for real-world applications like smartphones and airports.
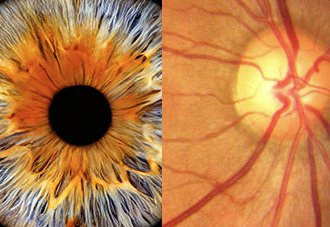
Advanced eye-based biometric technologies offer unparalleled security through unique biological patterns
When it comes to biometric identification, two advanced eye-based methods stand out: iris scans and retina scans. While both rely on the uniqueness of the human eye, they work in very different ways — using different eye structures, technologies, and scanning requirements. Here's a clear breakdown of how they work, how they differ, and which one is better suited for real-world use.
Quick Comparison Overview
Iris Scanning
- • Scans the colored part of the eye
- • Fast and contactless (1-2 seconds)
- • Works with glasses and contacts
- • Widely used in consumer devices
Retina Scanning
- • Maps blood vessels in the retina
- • Requires close contact (10+ seconds)
- • Extremely accurate but invasive
- • Limited to high-security applications
What Is an Iris Scan?
An iris scan captures an image of the colored part of the eye (the iris) using near-infrared (NIR) light and a dedicated infrared camera. This imaging reveals intricate iris patterns — like crypts, furrows, and rings — which are highly unique and remain stable over time.
Why Infrared Light?
Minimizes Reflections
Reduces glare on the eye's surface, improving pattern visibility
Enhances Contrast
Especially effective for dark-colored eyes with complex patterns
Low-Light Scanning
Works in various lighting conditions, ideal for airports and phones
Iris Scan Advantages
- Non-contact: No physical contact required
- Fast: 1–2 seconds for complete scan
- Flexible: Works with glasses, contacts, or partially covered eyes
- Portable: Can be integrated into consumer devices
Iris Scan Requirements
- Specialized Camera: Requires NIR cameras and software
- Processing Power: Needs biometric recognition algorithms
- Cost: Higher initial investment than basic cameras
What Is a Retina Scan?
A retina scan uses low-intensity infrared light to map the blood vessel pattern at the back of the eye — the retina. The user must place their eye close to a dedicated retinal scanner, where a beam of light is shined into the eye, and sensors capture how it's reflected.
How Retina Scanning Works
User positions eye close to scanner
Infrared light beam enters the eye
Light reflects off retinal blood vessels
Sensors capture unique vessel pattern
Retina Scan Advantages
- Extremely Accurate: Highest precision in biometrics
- Highly Secure: Nearly impossible to forge or replicate
- Stable Patterns: Blood vessel patterns remain constant
Retina Scan Limitations
- Invasive: Requires close proximity and eye contact
- Slow: 10+ seconds for complete scan
- Specialized Equipment: Requires dedicated retinal scanners
- Expensive: High cost limits widespread adoption
Key Differences: Side-by-Side Comparison
Comprehensive Technology Comparison
| Feature | Iris Scan | Retina Scan |
|---|---|---|
| Scans | Iris (surface, colored area) | Retina (internal, back of the eye) |
| Light Used | Near-infrared (non-visible) | Infrared (non-visible) |
| Equipment | Infrared camera + software | Retinal scanner with fixation beam |
| User Experience | Fast, contactless | Invasive, close-range |
| Speed | 1–2 seconds | 10+ seconds |
| Accuracy | Very High | Extremely High |
| Use Cases | Phones, airports, identity verification | Labs, military, secure research facilities |
Do You Need Special Equipment for Both?
Important: Both Require Specialized Hardware
Yes. Both technologies require dedicated devices and cannot be performed with regular smartphone or webcam cameras. However, iris scanners are smaller, cheaper, and easier to integrate into consumer or security devices — which is why they're far more common.
Iris Scan Equipment
Hardware Requirements
- • Near-infrared (NIR) camera or sensor
- • Infrared LED illumination system
- • Image processing unit
- • Biometric recognition software
Cost Range: $200 - $2,000 depending on accuracy and integration requirements
Retina Scan Equipment
Hardware Requirements
- • Medical-grade retinal scanner
- • Low-intensity infrared light source
- • Precision optical sensors
- • Eye positioning and fixation system
Cost Range: $5,000 - $50,000+ for professional-grade systems
Market Adoption and Integration
of biometric systems use iris scanning
adoption of retina scanning systems
deployment for iris systems
Market Analysis: Based on industry reports from MarketsandMarkets
Which One Is Better?
Iris Scans Win
For Most Applications
- Best Balance: Accuracy, comfort, and scalability
- High-Traffic: Perfect for airports, offices, and public spaces
- Consumer Integration: Easy to integrate into smartphones and devices
Retina Scans Excel
For Maximum Security
- Ultimate Security: Highest accuracy available in biometrics
- High-Security Facilities: Perfect for military and research labs
- Medical Applications: Can detect certain health conditions
The Verdict
Choose Iris Scanning For:
- • Consumer applications and devices
- • High-traffic environments (airports, offices)
- • Quick authentication needs
- • Cost-effective security solutions
- • User-friendly biometric systems
Choose Retina Scanning For:
- • Maximum security requirements
- • Military and government facilities
- • Research laboratories
- • Medical diagnostic applications
- • Low-volume, high-security access
Real-World Applications and Use Cases
Smartphones
Samsung Galaxy series uses iris scanning for secure device unlock
Iris TechnologyAirports
Border control and security checkpoints worldwide
Iris TechnologyMilitary Bases
High-security access control for classified areas
Retina TechnologyResearch Labs
Secure access to sensitive research facilities
Retina TechnologyHow Eye.Photo Enhances Iris Technology
Professional Iris Photography for Biometric Applications
Advanced Image Enhancement
- AI-powered reflection removal for clearer patterns
- Enhanced detail visibility for better recognition
- Optimized contrast for all eye colors
- 30-second processing for instant results
Professional Applications
- Security system integration
- Identity verification systems
- Professional iris photography
- Biometric research support
Frequently Asked Questions
Can regular cameras perform iris or retina scanning?
No, both technologies require specialized hardware. Iris scanning needs near-infrared cameras and specific software, while retina scanning requires medical-grade equipment with precision optical sensors. Regular smartphone or webcam cameras cannot capture the necessary detail or use the required infrared light.
Which is more accurate: iris scanning or retina scanning?
Retina scanning is slightly more accurate with virtually zero false positives, but iris scanning is extremely accurate as well (1 in 10^12 false match rate). For practical purposes, both provide excellent security, but iris scanning's speed and user-friendliness make it more suitable for most applications.
Are these scanning methods safe for your eyes?
Yes, both methods are completely safe. They use low-intensity infrared light that doesn't harm the eye. The light levels are well below safety thresholds established by medical authorities. Many people use iris scanning daily on their smartphones without any issues.
Can these technologies work with glasses or contact lenses?
Iris scanning works well with glasses and most contact lenses, as it only needs to see the iris surface. Retina scanning may have issues with certain types of contact lenses or thick glasses that interfere with the light beam reaching the retina. This is another advantage of iris scanning for everyday use.
What happens if someone has an eye injury or surgery?
Minor injuries typically don't affect the scanning process, as both technologies look at stable structural patterns. However, major eye surgery or trauma could potentially alter the patterns. Most systems can be re-enrolled with updated biometric data if needed.
Final Thoughts
Both iris and retina scans are marvels of biometric technology, offering unmatched security based on your unique eye structure. But with easier hardware integration and faster, user-friendly operation, iris scanning is the clear winner for most real-world applications.
As biometric technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more sophisticated iris scanning systems that are faster, more accurate, and easier to integrate into our daily lives. Whether you're securing your smartphone, accessing your office, or passing through airport security, understanding these technologies helps you appreciate the incredible science behind modern security systems.
Ready to Explore Advanced Iris Technology?
Discover how Eye.Photo's AI-enhanced iris photography can support your biometric applications and security needs.
